Disease | Modeling approach | Animal strains | Measurements |
Oral ulcer | Induced by chemical cauterization | SD/Wistar rat | Observation of the morphological and area of ulcer surface |
immune-induced method | SD/Wistar rat |
Liver disease | CCl4 induced liver fibrosis | SD/Wistar rat | Detect Serum biochemical markers and histopathology, steatosis, significant fibrous septum formation in the portal area |
Acute liver injury model induced by D-Gal combined with LPS | SD/Wistar rat C57BL/6 mouse | Histological examination of livers identified hepatocyte necrosis with an influx of inflammatory cells; leukocyte infiltration and MPO increased; the activities of AST and ALT in serum increased ;TNF-α increased |
Concanavalin A- induced Hepatitis Model | C57BL/6 mouse BALB/c mouse | AST, ALT, TNF-α, IFN-γ increased; Histopathology analysis of liver leukocytes infiltration; Hepatic necrosis and liver fibrosis |
Bile duct ligation (BDL) | SD/Wistar rat | Detect Serum biochemical markers and histopathology, pseudolobule formation |
Alcohol-induced cirrhosis | SD/Wistar rat |
Stomach disease | Acetic acid-induced gastric ulcer | SD/Wistar rat | ulcer degree, inflammatory cytokines, gastric histopathology analysis |
Gastric adenocarcinoma induced by MNNG combined with ranitidine |
Helicobacter pylori infection induces gastritis | C57BL/6 mouse BALB/c mouse | Serum inflammatory factor analysis, gastric histopathological analysis, helicobacter pylori detection |
Diarrhea | Diarrhea induced by senna leaf | SD/Wistar rat | Diarrhea rate and diarrhea index |
Ulcerative colitis | TNBS induced ulcerative colitis | SD/Wistar rat | Body weight changes, colonic histopathological analysis, presence or absence of hematocele |
DSS induced ulcerative colitis | SD/Wistar rat |
Colorectal cancer | AOM-DSS induced inflammatory colorectal cancer | C57BL/6 mouse BALB/c mouse | Observe for the presence of a colonic tubular adenoma |
Pancreatitis | retrograde injection of sodium taurocholate into the pancreatic‑bile duct | SD/Wistar rat | The serum levels of lipase and amylase increased; Interstitial edema, necrosis of acinar cells and infiltration of inflammatory cells in pancreatic tissue |
TOPBIOTECH can provide customized animal disease model services according to customers' requirements |
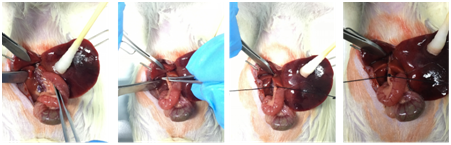
Case analysis Bile duct ligation rat model
In the liver, the experimental obstruction of the extrahepatic biliary system initiates a complex cascade of pathological events that leads to cholestasis and inflammation resulting in a strong fibrotic reaction originating from the periportal fields. Therefore, surgical ligation of the common bile duct has become the most commonly used model to induce obstructive cholestatic injury in rodents and to study the molecular and cellular events that underlie these pathophysiological mechanisms. Both cannulation/obstruction and ligation induced a high yield of cirrhosis in rats with morphological changes that were comparable to those observed in human biliary cirrhosis.
Experimental animal information |
Name of animal model | Bile duct ligation rat model |
Species and strains of animal | SD/Wistar rat |
Gender of animal | ♂ |
Age of animal | adult |
Weight of animal | 200~250g |
Caracteristics
The levels of ALT、AST、TBIL、DBIL in serum were significantly increased, the livers of animals that received BDL show architectural alterations that are mainly characterized by the formation of edema and fibrotic nodules on the surface of corresponding livers and hydrops of the gall bladder that is filled with large quantities of bile.
Partial surgical process display