Your Current Position: Technology service
Search
-
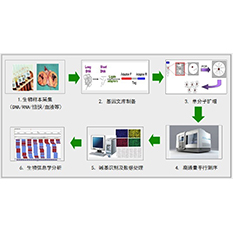
High throughput sequencing (High-throughput sequencing), also known as "next generation" sequencing, which can sequence hundreds of thousands to millions of DNA molecules in parallel.
-
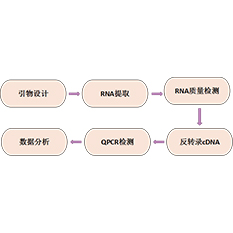
Real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR (PCR) is a method of adding fluorescent groups to PCR reaction system and using fluorescence signal accumulation to real-time monitor the total amount of products after each (PCR) cycle of polymerase
-
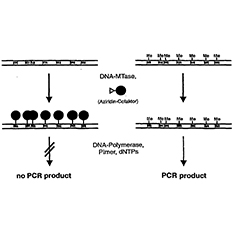
DNA methylation is refer to change 5’cytosineof CpG dinucleotide to methylcytosine through induced by DNA methyltransferase (DNMTs) , and is one of the earliest approaches.
-
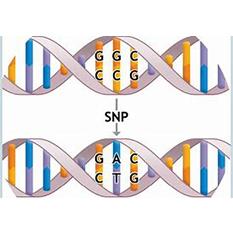
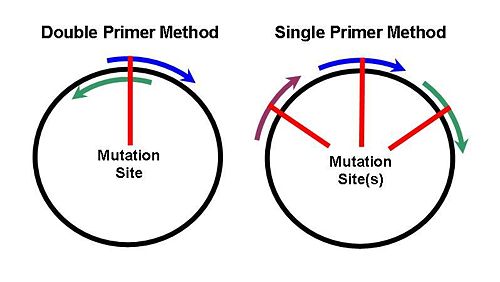
Site-directed mutagenesis is the introduction of desired changes (usually changes in the favorable direction) into the desired DNA fragments (either genome or plasmid) by means of polymerase chain reaction (PCR),
-
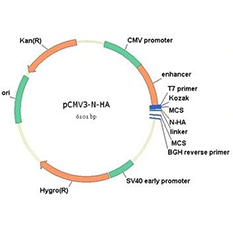
Vector construction is to transport the target DNA molecule to the recipient cells, so we must find a carrier that can enter the cell and load the foreign DNA fragment into the cell, and still copy it in the same way.
-
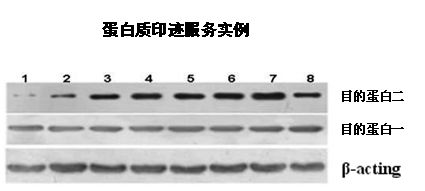
Western blotting is an important technique used in cell and molecular biology. By using a western blot, researchers are able to identify specific proteins from a complex mixture of proteins extracted from cells
-
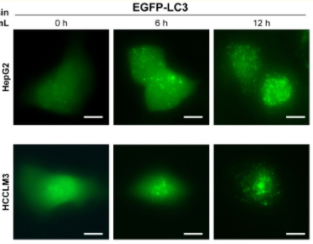
Autophagy or autophagocytosis: also known as type II cell death, is a process in which cells degrade their damaged organelles and macromolecules by using lysosomes under the regulation of autophagy related gene (ATG).